Information
1.Modern Magnet Materials
2.Manufacturing Methods
3.Surface treatment
4.Comparison Table of Different Coating types
5.Magnetization
6.Safety principle for manual operation
1.Modern Magnet Materials
There are four classes of modern commercialized magnets, each based on their material composition. Within each class is a family of grades with their own magnetic properties. These general classes are:Neodymium Iron Boron
Samarium Cobalt
Ceramic
Alnico
2.Manufacturing Methods
Permanent magnets are manufactured by one of the following methods:Sintering, (Rare Earths, Ceramics, and Alnicos)
Pressure Bonding or Injection Molding, (Rare Earths and Ceramics)
Casting, (Alnicos)
Extruding, (Bonded Neodymium and Ceramics)
Calendering (Neodymium and Ceramics)
3.Surface treatment
Samarium Cobalt, Alnico, and Ceramic materials are corrosion resistant, and do not require to be coated against corrosion. Alnico is easily plated for cosmetic qualities.Neodymium Iron Boron magnets are susceptible to corrosion and consideration should be given to the operating environment to determine if coating is necessary. There are a variety of coatings suitable for permanent magnets, Not all types of coating will be suitable for every material or magnet geometry, and the final choice will depend on the application and environment. An additional option is to house the magnet in an external casing to prevent corrosion and damage.
4.Comparison Table of Different Coating types
|
Surface |
Coating |
Suggested Environment Temperature |
THK (μm) |
Color |
Salt Spray Test |
Temperature & |
Resistance of |
Resistance effect |
|
Passivation |
|
<80℃ |
<1 |
Silver Grey |
Worse |
very poor (24Hrs) |
Very Poor |
for temporary storage and short term transporation |
|
Nickel |
Ni+Ni |
<200℃ |
15-25 |
Bright Silver |
48 |
Good |
Fair |
Excellent against Humidity and |
|
Nickel |
Ni+Cu+Ni |
<200℃ |
15-25 |
Bright Silver |
72 |
Very Good |
Fair |
The most popular coating type with |
|
Zinc |
Zn |
<150℃ |
7-15 |
Bright Blue |
24 |
Very Poor (24Hrs) |
Porr |
Poor protective capability and for common environment only |
|
Zinc |
C-Zn |
<150℃ |
7-15 |
Shinny Color |
48 |
Poor(48Hrs) |
Fair |
good protective capability for industrial enviroment |
|
Tin |
Ni+Cu+Sn |
<150℃ |
15-25 |
Silver |
72 |
Very Good |
Fair |
Superior Against |
|
Gold |
Ni+Cu+Au |
|
10-20 |
Gold |
|
|
|
Superior Against Humidity |
|
Copper |
Ni+Cu |
|
10-20 |
Gold |
|
|
|
Temporary Protection |
|
Epoxy |
Epoxy |
<130℃ |
15-25 |
Black, Red, Grey |
96 |
Good |
Very Good |
Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray |
|
Epoxy |
Ni+Cu+Epoxy |
<130℃ |
15-25 |
Black, Red, Grey |
96 |
Good |
Very Good |
Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray |
|
Epoxy |
Zn+Epoxy |
<130℃ |
15-25 |
Black, Red, Grey |
96 |
Good |
Very Good |
Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray |
|
Chemical |
Ni |
|
10-20 |
Silver Grey |
|
|
|
Excellent Against Humidity |
|
Parylene |
Parylene |
|
5-20 |
Grey |
|
|
|
Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray |
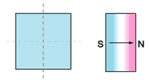
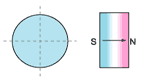
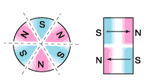
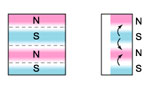
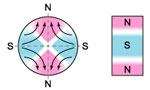
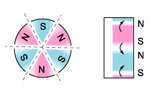
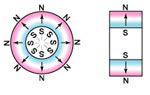
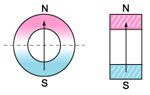
5.Magnetization
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
oriented through thickness |
axially oriented |
axially oriented in segments |
|
|
|
|
|
oriented laterally |
multipole oriented in segments on outside diameter* |
multipole oriented in segments on one face |
|
|
|
|
|
radially oriented * |
oriented through |
multipole oriented in segments on inside diameter* |
|
|
|
all available as isotropic or anisotropic material |
|
* only available in isotropic and certain anisotropic materials only |
|
radially oriented |
diametrical oriented |
6.Safety principle for manual operation
1. The magnetized permanent magnets with strong magnetic field attract the iron and other magnetic matters around them greatly. Under common condition, the manual operator should be very careful to avoid any damage. Due to the strong magnetic force, the big magnet close to them takes the risk of damage. People always process these magnets separately or by clamps. In this case, we should ware the protection gloves in operation.2. In this circumstance of strong magnetic field, any sensible electronic component and test meter may be altered or damaged. Please see to it that the computer, display and magnetic media , for example the magnetic disc ,magnetic cassette tape and video record tape etc., are far from the magnetized components, say farther than 2m.
3. The collision of the attracting forces between two permanent magnets will bring enormous sparkles. Therefore, the flammable or explosive matters should not be placed around them.
4. When the magnet is exposed to hydrogen, it is prohibited to use permanent magnets without protection coating. The reason is that the sorption of hydrogen will destroy the microstructure of the magnet and lead to the deconstruction of the magnetic properties. The only way to protect the magnet effectively is to enclose the magnet in a case and seal it.